Tutorial: Recover RAID Data with RAID Recovery Software
What is RAID Recovery
Users need a RAID recovery for the same reasons they need normal hard disk data recovery: human errors, hardware or software failure, malware infection, mechanical errors, power outage, bad sectors, or abrupt system shutdown can all cause a broken or corrupted RAID. However, recovering a broken RAID presents a unique challenge.
When a RAID is damaged, the RAID volume becomes inaccessible and data is lost. However, you can't access or recover data directly from RAID hard drives. To recover lost data, you need to reconstruct or rebuild the RAID configuration, which can be a difficult process. Fortunately, there are third-party data recovery software available that can simplify this process.
Best RAID Recovery Software - Deep Data Recovery
Choosing a professional RAID recovery software is greatly helpful in recovering data from RAID drives. Deep Data Recovery provides complete RAID data recovery solutions under Windows, allowing you to recover data from any RAID configuration, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10, as long as your computer system can recognize the drive.
- Recommendation
- Recover data from multiple RAID levels
- Recover files from failed RAID drives
- Recover lost or formatted RAID logical volumes
How to Recover Data from RAID Hard Drive
Don't hesitate to equip your computer with this powerful tool. It allows you to recover files from a RAID hard drive with a simple 3-step process.
Scan disks > Preview and select wanted files > Recover data.
To recover RAID data with the help of Deep Data Recovery, follow these steps: First, download and install the Deep Data Recovery software on your computer. Next, launch the software and select the RAID drive from which you want to recover data.
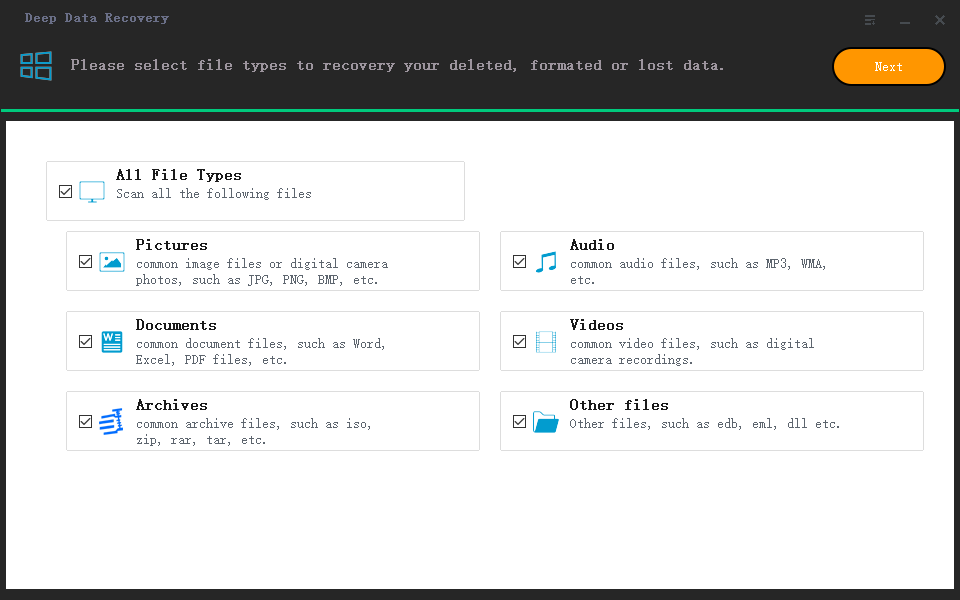
Step 1. Select file types
Launch Deep Data Recovery software on your PC, select the desired file types, and click "Next" to initiate the recovery process.
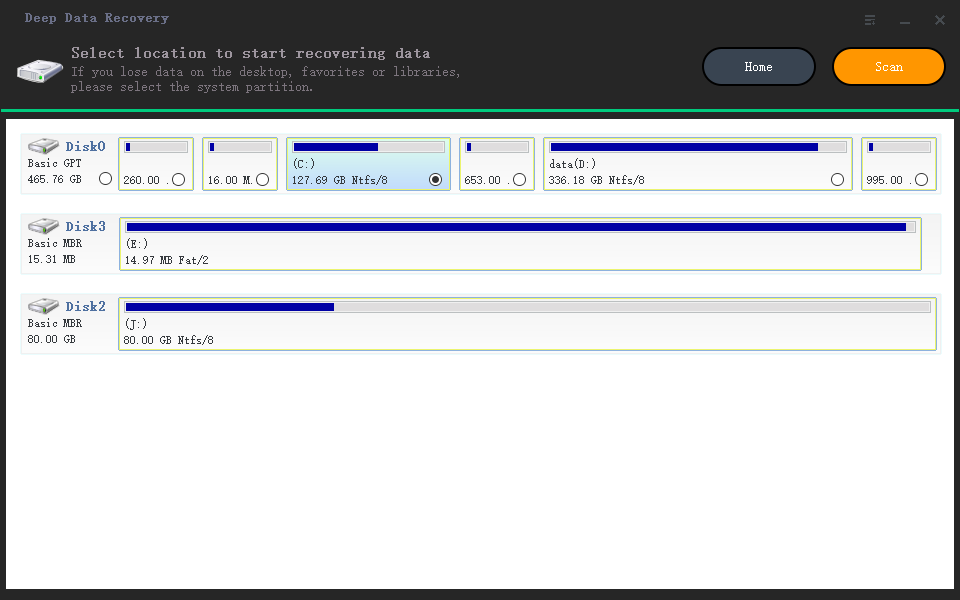
Step 2. Scan the RAID drive
Choose the RAID drive you want to recover data from, click "Scan", and wait for the scanning process to finish, which will display the deleted files one by one.
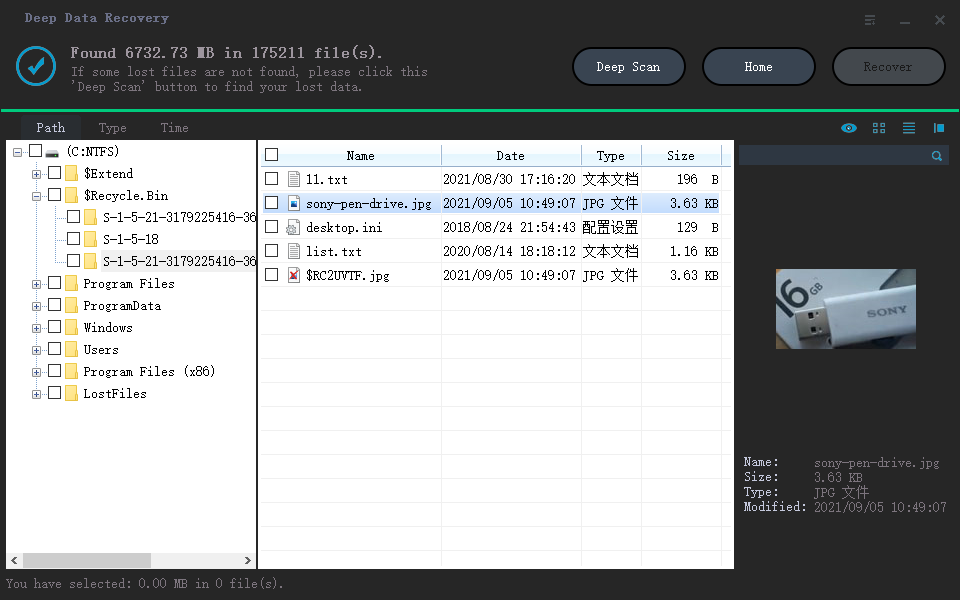
Step 3. Find and preview lost RAID files
You can use "Filter" to quickly find deleted or lost files, and also use Search to find lost RAID drive files by their file name or extension.
Step 4. Restore lost RAID drive files
Select the wanted files and click "Recover". Browse to save these files to another secure location.
In addition to its RAID data recovery capabilities, Qiling data recovery software also offers other features, allowing users to recover data in various other scenarios.
- Recover files from various storage devices, including common hard drives, external hard drives, SD cards, USB flash drives, and other conventional storage media.
- Data recovery software can help recover permanently deleted files, system crash, OS reinstallation, and other challenging data loss situations by scanning the device for recoverable data, identifying and extracting the deleted files, and restoring them to their original location or a designated recovery folder. This process can be performed on various devices, including computers, laptops, and external storage devices, and can be used to recover data from different file systems and operating systems.
- This tool allows you to extract and recover various file types, including photos, videos, audio files, Microsoft Office files, Adobe files, and over 200 other file formats.
Consult with Qiling data recovery experts for one-on-one manual recovery service, which includes a free diagnosis. Our experienced engineers can repair damaged RAID structures and restore data from all RAID levels.
- Data can be restored from all RAID levels, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, and others, using specialized software and hardware tools. These tools allow for the recovery of data from failed or damaged RAID arrays, and can often recover data even if multiple drives in the array have failed.
- To recover data from enterprise RAIDs, you'll need a specialized tool that can read the data from the RAID configuration, which is often proprietary and not easily readable by standard data recovery tools. One such tool is the "QNAP Data Recovery" software, specifically designed for QNAP NAS devices, which can recover data from QNAP, Synology, WD, Buffalo, and other enterprise RAIDs.
- Retrieve lost RAID data caused by any issues
- Fix disks that become GPT protected partitions
- Recover data from RAID remotely, no need to ship
General Knowledge About RAID
Before diving into professional RAID data recovery software, it's essential to understand the basics of RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks). RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple physical disks into a single logical unit, providing improved performance, reliability, and capacity.
Definition of RAID
RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks or Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that stores the same data in different places on multiple physical hard disks, increasing system performance or providing fault tolerance.
Different Levels of RAID
Data is allocated on RAID hard drives in different ways, referred to as RAID levels, including RAID 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 10. RAID levels allocate data in various configurations, with RAID 0 offering striping for improved performance, RAID 1 providing mirroring for redundancy, RAID 5 combining striping and parity for a balance of performance and redundancy, and RAID 10 offering a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0 for added redundancy and performance.
| Level | Definition |
|---|---|
| RAID 0 | RAID 0 provides data striping across multiple disk drives, improving performance, but it does not offer redundancy, making it vulnerable to data loss if one drive fails. |
| RAID 1 | RAID 1 provides disk mirroring, doubling the read speed and maintaining the same write speed as a single disk. |
| RAID 5 | RAID 5 is a popular storage configuration that provides excellent performance and good fault tolerance by striping data at the byte level and incorporating error correction information. This setup makes it one of the most widely used RAID levels, highlighting the importance of backing up RAID drives to prevent complete data loss. |
| RAID 6 | RAID 6 requires a minimum of four disks, using two parity stripes on each disk, allowing for two disk failures within the RAID set, providing high fault tolerance but being more expensive due to the two extra disks required for parity. |
| RAID 10 | RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a level of RAID that combines two RAID 0 stripes with a RAID 1 mirror, providing both data replication and sharing among disks. |
Advantages of RAID
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) uses multiple disks working together to increase overall system performance, especially for server users. This setup also provides additional benefits, including increased storage capacity and data redundancy, which can help protect against data loss in case of a disk failure.
- Higher data security
- Higher fault tolerance
- Regularly performing parity checks and monitoring the system for any potential crashes is crucial to maintain system stability and prevent data loss. This involves verifying the integrity of data and ensuring that all system components are functioning correctly.
- Simultaneous reading and writing process
While RAID provides higher data security, data loss can still occur on RAID hard drives due to system crashes, virus attacks, power failures, or other unexpected errors. Fortunately, with the right RAID recovery software, you can recover your data from RAID hard drives safely and effectively, making the process relatively easy.
Related Articles
- Fix Windows Update Error 0x80240034
- Fix Error Code 0x800F0954 on Windows 10
- The Add-In Template Is Not Valid in Word? 4 Fixes Here!
- All You Need to Know About a Rooted Device